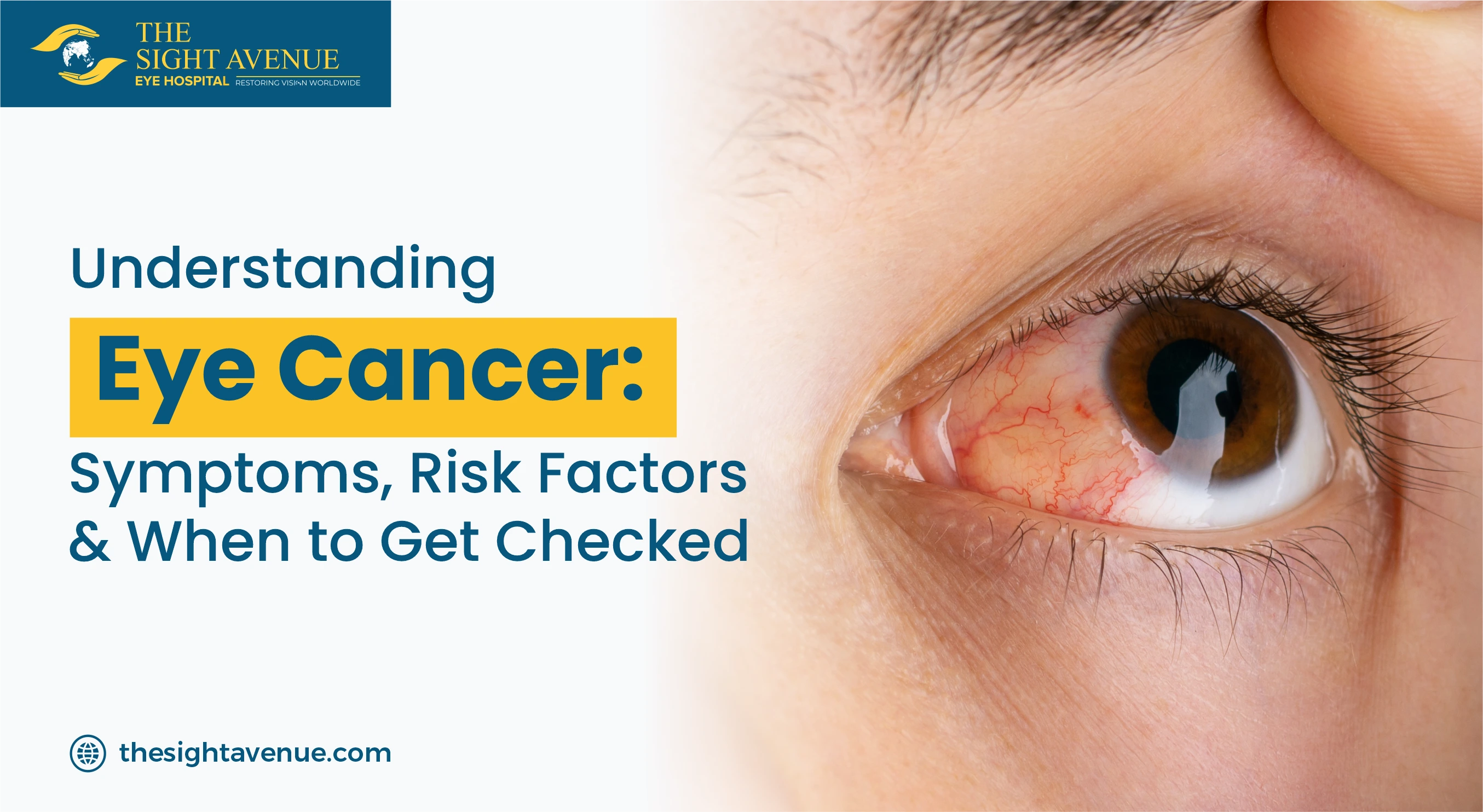
Double Vision (Diplopia): What It Is, Causes & Treatment

Are you having trouble seeing, and when you look at one object, it appears to have two images at the same time? Then you might have a big chance of facing double vision or diplopia. However, this can be a temporary or long-term issue and may indicate underlying health problems. But understanding what diplopia is, its causes, and its treatment can help you overcome this common condition.
What is Double Vision (Diplopia)?
Double vision usually occurs when the eyes are unable to work together correctly, which causes overlapping or duplicate images. It can affect one eye (monocular diplopia) or both eyes (binocular diplopia), and the severity can differ from mild to debilitating depending on the person 's current condition.
Types of Diplopia
1. Monocular Diplopia: Persists even when one eye is closed, often due to corneal or lens issues.
2. Binocular Diplopia: Occurs only when both eyes are open, typically caused by misalignment of the eyes.
Symptoms of Double Vision
- Two Overlapping Images: These may appear side by side, on top of each other, or diagonally.
- Eye Strain and Headaches: The constant effort to focus can lead to discomfort.
- Blurry Vision: Difficulty in distinguishing objects clearly.
- Dizziness and Balance Issues: Confusion caused by seeing double can affect spatial awareness.
- Sensitivity to Light: Bright lights may intensify discomfort or strain.

What Causes Double Vision?
Double vision can stem from various underlying conditions, ranging from minor issues to serious medical concerns. Below are the common causes:
1. Eye Muscle Problems
- Weak or paralyzed eye muscles can lead to misalignment, causing binocular diplopia.
- Conditions like Strabismus (Crossed Eyes) or thyroid eye disease may contribute.
2. Corneal Issues
- Scars, dryness, or irregularities in the cornea can cause monocular diplopia.
- Keratoconus, where the cornea thins and bulges, is a common culprit.
3. Lens Abnormalities
- Cataracts can distort light entering the eye, leading to double images.
- Refractive errors like astigmatism may also contribute.
4. Neurological Conditions
- Neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis, stroke, or brain tumors can interfere with eye coordination.
- Damage to the cranial nerves that control eye movement is another cause.
5. Trauma or Injury
- Head injuries or direct trauma to the eyes can disrupt normal vision.
- Fractures in the eye socket may impair eye alignment.
6. Systemic Diseases
- Diabetes, high blood pressure, or autoimmune diseases like myasthenia gravis can lead to diplopia.
Diagnosing Double Vision
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s how doctors typically identify the condition:
1. Comprehensive Eye Exam
An ophthalmologist will assess your vision, eye alignment, and movement.
2. Medical History Review
Understanding your overall health, any recent injuries, or pre-existing conditions helps pinpoint the cause.
3. Imaging Tests
CT scans or MRIs may be used to detect structural or neurological abnormalities.
4. Blood Tests
In cases where autoimmune diseases or infections are suspected, blood tests may be required.
Treatment Options for Double Vision
The treatment for diplopia or double vision depends on its underlying causes. Here’s a breakdown of the common approaches:

1. Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses
- Specialized lenses or prisms can correct refractive errors or misalignment.
- Temporary use of an eye patch may help manage symptoms.
2. Medications
- Steroids: Used to reduce inflammation in autoimmune or neurological conditions.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for infections causing diplopia.
- Diabetic Management: Controlling blood sugar levels can resolve vision issues related to diabetes.
3. Surgery
- Eye muscle surgery can correct alignment issues, especially in strabismus.
- Cataract surgery may be necessary to address lens-related problems.
- Repair of orbital fractures or other trauma-related issues might also be required.
4. Vision Therapy
- Eye exercises and therapies can help improve coordination and focus.
- These are particularly effective in children with strabismus or lazy eye.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Managing chronic conditions like diabetes or thyroid issues can reduce the risk of double vision.
- Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms, like prolonged screen time, can provide relief.
When to See a Doctor
While occasional double vision may not be a cause for concern, persistent or recurring symptoms should prompt a visit to an eye care professional. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Sudden onset of double vision.
- Severe headaches or nausea accompanying vision changes.
- Difficulty speaking, walking, or balancing.
- Eye pain or redness.
Living with Double Vision: Tips and Precautions
- Use Proper Lighting: Dim lighting can strain your eyes; ensure adequate brightness in your surroundings.
- Follow Prescribed Treatment: Stick to your doctor’s recommendations for medications or therapies.
- Take Breaks from Screens: Regular breaks can prevent further eye strain.
- Protect Your Eyes: Wear safety glasses in environments prone to eye injuries.
Conclusion
Double vision (diplopia) is more than just an inconvenience—it can be a sign of underlying health conditions that require attention. By understanding symptoms, causes, and treatment options for diplopia, you can take necessary steps toward managing this condition.
If you’re experiencing persistent double vision, don’t delay seeking professional help; feel free to visit The Sight Avenue Hospital (the best eye hospital in Gurgaon). Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help restore clear, single vision and improve your quality of life.
Eye problems? Searching for an eye specialist near me in Delhi NCR? The Sight Avenue has 5 eye clinics in Delhi NCR. Contact us today!
Eye Hospital in Delhi
- The Sight Avenue
- The Sight Avenue
- The Sight Avenue
E-82-A, Ground Floor, Hansraj Gupta Rd, Greater Kailash I, New Delhi, Delhi 110048
Email:enquiry@thesightavenue.com
Tel : 011-4666 0666
Mob : +91-8883330799
Fortis Hospital, Escorts Okhla, New Delhi
Fortis Hospital, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi
Recent Post